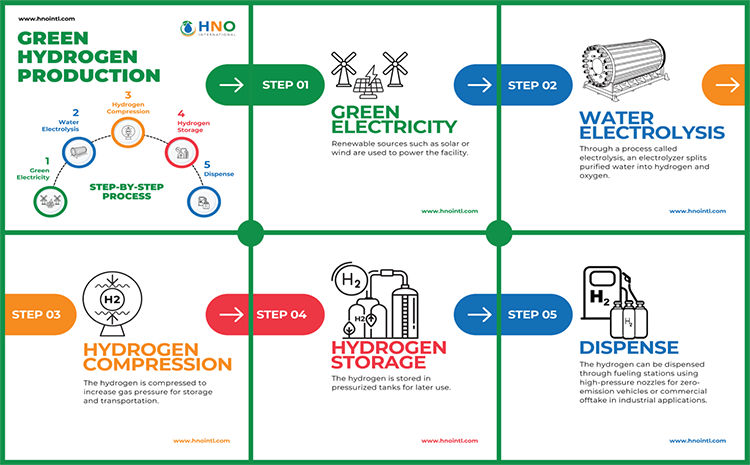
The Green Hydrogen Production Process
In the quest for sustainable energy sources, hydrogen has emerged as a promising contender, offering a pathway towards a cleaner, greener future. But how exactly does hydrogen production work? There are many ways hydrogen can be produced. Let’s delve into the intricate process of green hydrogen:
1. Green Electricity as Feedstock
At the heart of green hydrogen production lies renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, or hydroelectric power. These sources provide the essential electricity needed to kickstart the process. Unlike traditional methods that rely on fossil fuels, green hydrogen production harnesses the power of clean, renewable electricity, minimizing carbon emissions from the get-go.
2. Alkaline Electrolysis
Next comes alkaline electrolysis, a fundamental technique that separates purified water into its constituent elements: hydrogen and oxygen. This process involves passing an electric current through water, causing it to split into hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The hydrogen ions are then attracted to the cathode, where they combine to form hydrogen gas (H2), while oxygen gas (O2) is released at the anode. Through this method, we obtain high-purity hydrogen without the carbon footprint associated with traditional production methods.
3. Hydrogen Compression
Once the hydrogen is produced, it needs to be compressed for efficient storage and transportation. Compression involves reducing the volume of hydrogen gas while increasing its pressure. This step ensures that hydrogen can be stored safely and transported.
4. Hydrogen Storage
Hydrogen can be stored in various forms, including compressed gas, liquid hydrogen, and solid-state. Each method comes with its own advantages and challenges, but the ultimate goal is to have a storage solution that is both safe and cost-effective for your needs, enabling widespread adoption of green hydrogen as an energy carrier.
5. Dispensing and Utilization
Finally, the produced hydrogen can be dispensed through high-pressure nozzles for refueling vehicles or for commercial offtake in industrial applications. Whether it’s powering fuel cell vehicles or serving as a feedstock for industrial processes, green hydrogen offers a versatile and sustainable alternative to conventional fossil fuels.
In conclusion, green hydrogen production offers a beacon of hope in our transition towards a low-carbon future. By leveraging renewable energy sources and innovative technologies, we can harness the power of hydrogen to drive sustainable development and combat climate change. As we continue to refine and scale up the production process, green hydrogen holds the potential to revolutionize the way we power our world, paving the way for a cleaner, greener tomorrow.